The frame structure is widely used in engineering and often seen in large and medium-sized buildings such as stations, ports, and industrial and mining areas. This structure has the characteristics of large span and small load. In this article, we simulate this type of structure to reveal the deformation and stress under its body force using WELSIM.
Physical model
The applications of frame structure can be seen on various occasions. The design of the frame, especially the stability of the structure are critical.


The types are frame structure are also varied, and each design has its advantages. A schematic view of the frame structure designs is shown as follows:

Finite Element Analysis Model
Now, we import the designed frame structure model from CAD software into WELSIM software and conduct the subsequent analysis.
It can be seen that the imported geometry is a multi-body structure, as it is assumed here that welding or riveting make this structure, and the material is generally the same for bodies. We combine all bodies to eliminate the need for contact setup steps and save computing time. WELSIM provides the Boolean operation features. You can press the “Union” button from the toolbar or menu bar.
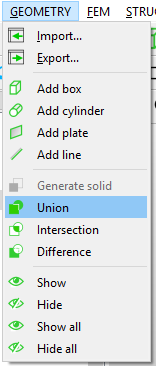

As the structure is merged, you get a combined body as shown in the picture below. Here we assign the default structural steel material to the structure.
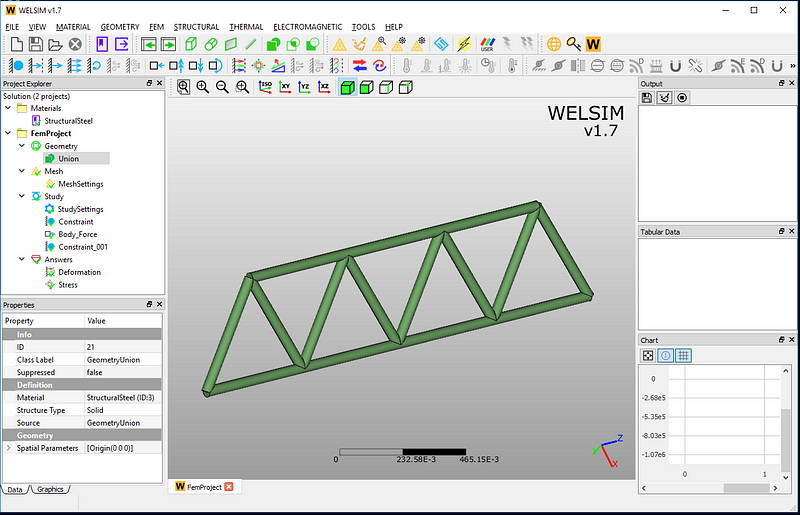
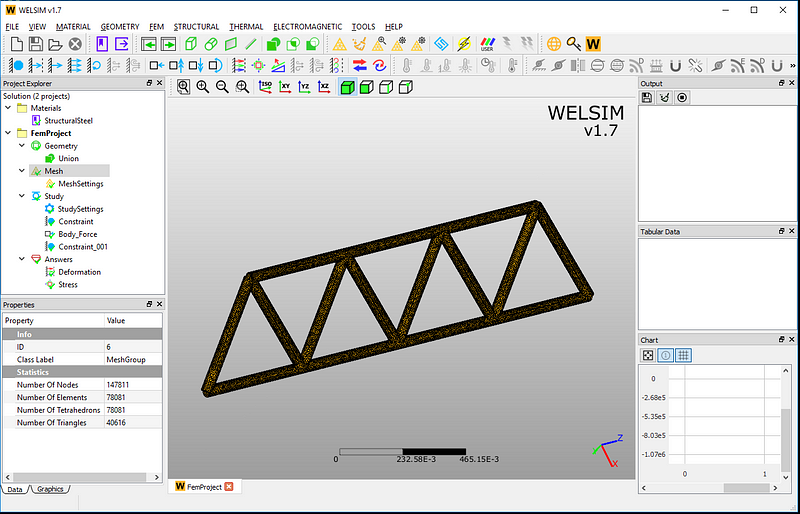
Mesh
WELSIM provides an automatic meshing function. With a simple setting, you can quickly get the generated elements and nodes. Here we set to mesh the domain with the Tet10 element type. The results of meshing are as follows. There are 147,811 nodes and 78,081 tetrahedral elements.
Boundary conditions and loads
In this analysis, we impose two fixed supports on the bottom.
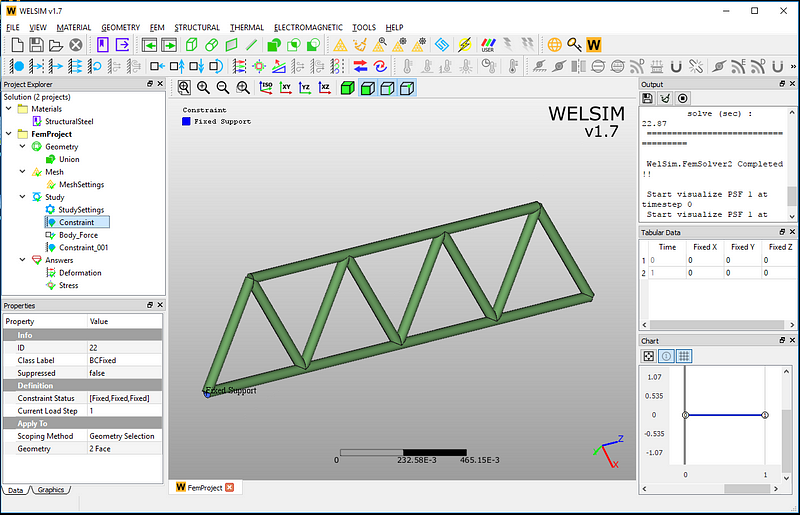
Next, we enter the body force that represents the weight of the frames. The body force is a force that acts on the entire structure. Such forces can be caused by the gravity, electric fields, and magnetic fields. The body force is not the same as the contact force or surface force exerted on the surface of an object. Some virtual forces, such as centrifugal force, Euler force and Coriolis effect, also belong to body force.
Like surface forces, the body force is also a directional vector force. It can be regarded as the product of the force density and mass. The formula is as follows:

WELSIM supports the body force input. Users can find the related buttons from the toolbar or menu bar as shown in the figure.

In the graphic selection window, users can activate different selection modes including volume, surface, edge, and vertex selection.

Since the body force acts on the entire body, we activate the selection of the volume and select the geometries from the graphics window. Here we set the magnitude of the body force to 1e6 with the direction of -X.
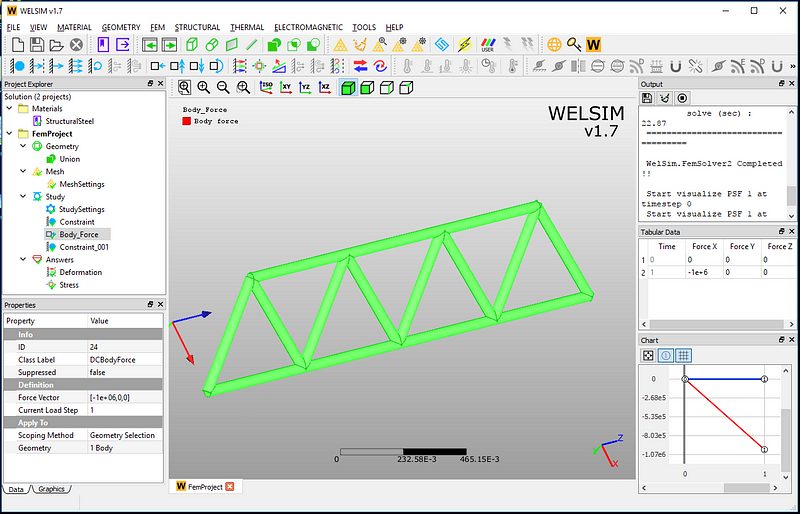
Solution and Results
Click the Solve button, and you’ll be able to solve the model quickly. The maximum total deformation is 2.793e-3, and the maximum Von-Mises stress is 1.669e8.
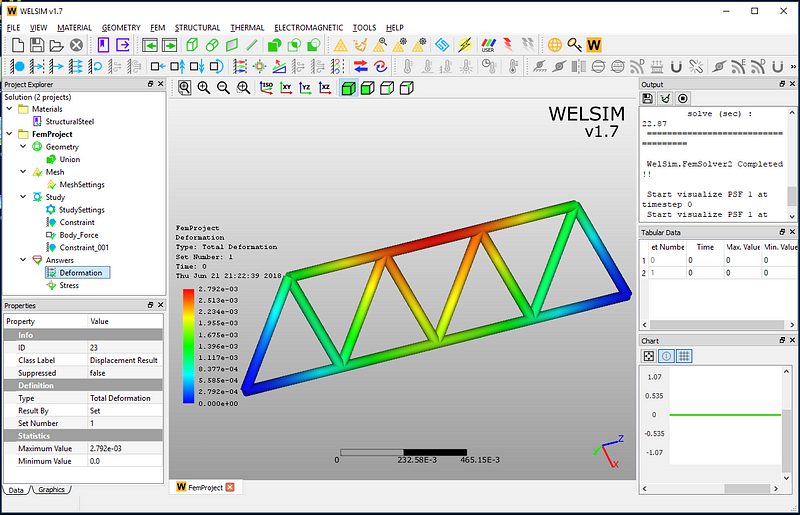
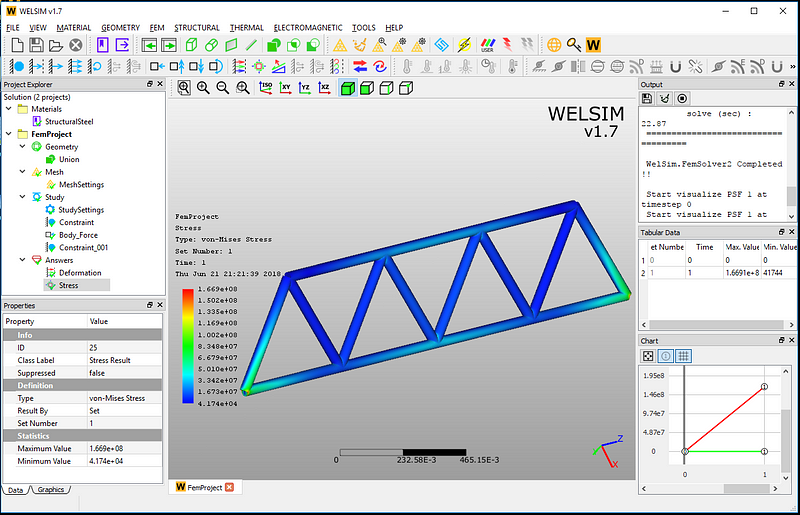
The result contours show the total deformation and the von-Mises stress of the given frame structure. Now user can clearly understand the deformation and stress status of the designs under the body force effects. You also can evaluate other analysis results such as strain, reaction force at the support positions.
Note: Body force feature is newly introduced to the version 1.7 of WELSIM.