Linux SSH provides powerful remote access capabilities. Users can quickly access other Linux machines, such as clusters, using SSH commands. Now let’s take a look at SSH and how to apply SSH to run the graphical application remotely.
What is SSH?
SSH is a network protocol used for encrypted logins between computers. If a user logs in to another remote computer from the local machine using the SSH protocol, we can assume that the login is secure.
It should be pointed out that SSH is just a protocol, and there are multiple implementations, both commercial and open source. The implementation for this article is OpenSSH, which is free software and has a wide range of applications.
Basic usage
1) Login
Log in to a remote host, and the common format is as follows:
ssh [-l username] [-p port] [username@] hostname or IP address
Details can be viewed using ssh -h. If you do not specify a user, you will be logged in by default using the root account. Such as:
ssh 23.239.28.120
Designated user:
If you have modified the ssh login port, you can:
ssh -p 12333 [email protected]
2) Uploading files
The basic statement for uploading files to a remote machine is as follows:
scp localfile username@remote machine IP address: filedirectory
3) Download file
The basic statement for downloading files from a remote machine is as follows:
scp username@remote machinename or IP: remotefile localfolder
An example of SSH remote access
Now Let’s remotely access a Linux machine and run a graphical application on the server to calculate and save the file.
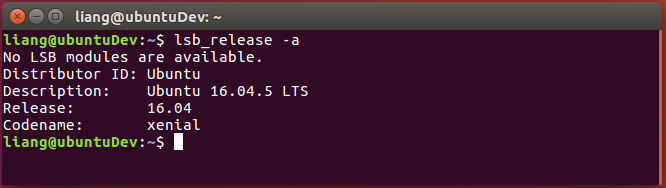
First, understand the information of this machine. enter:
lsb_release -a
The native system is Ubuntu 16.04.5 LTS:
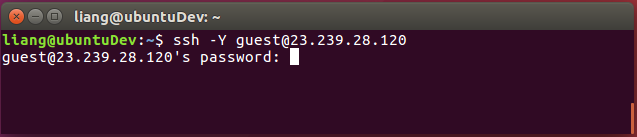
Log in to the guest account of the remote server at 23.239.28.120 by SSH. Enter following in the terminal window:
ssh -Y [email protected]
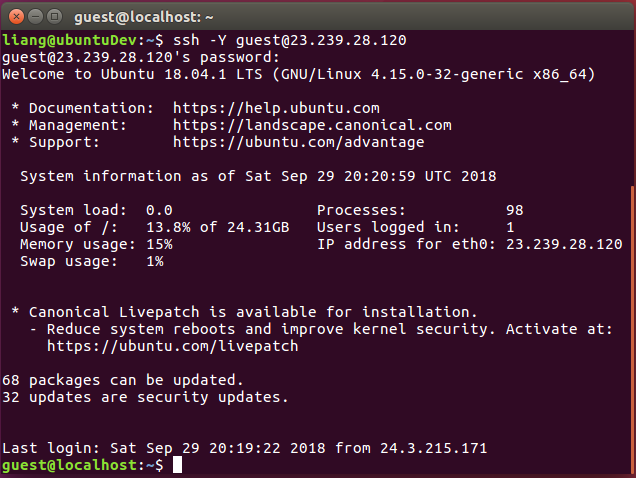
If the server is online and the user exists, you will be asked to enter the password. The password is welsim and you can enter the password and hit the return key. Once you successfully log in to the remote machine, you will see the system information of the remote server.
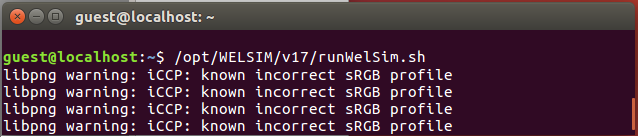
Since the Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) software WELSIM has been installed on the remote machine. Similar to using the software locally, you can type in the command line:
/opt/WELSIM/v17/runWelSim.sh
Then the application starts as shown below:
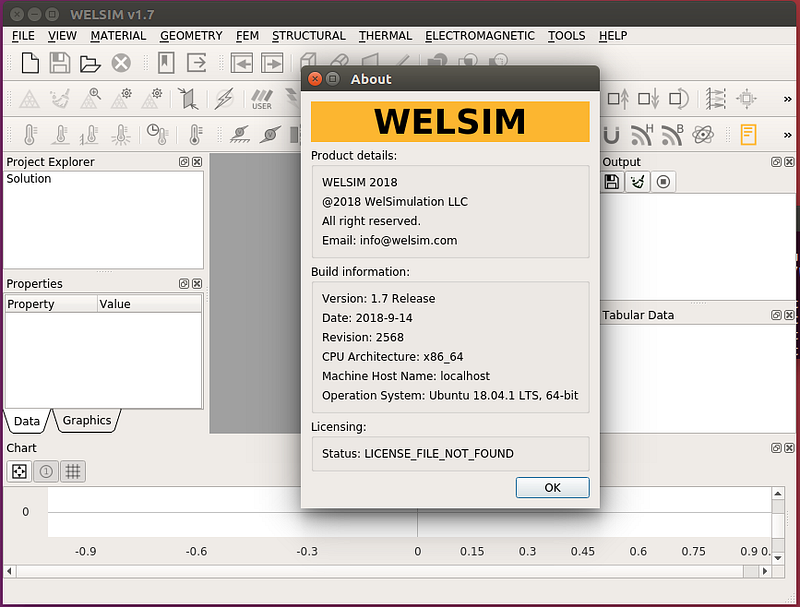
The remote WELSIM GUI shows up, and you can view the software related information shown in the figure below. The information page shows the server is an Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS 64-bit Linux machine, which is consistent with the remote server information.
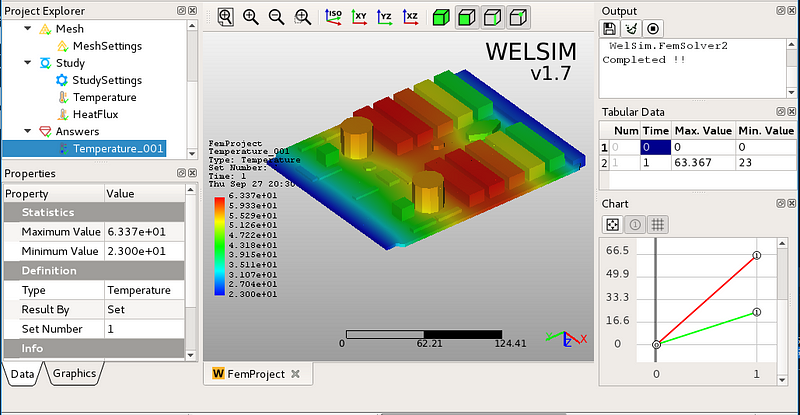
Users can run WELSIM application to conduct the finite element analysis. As shown in the figure below, it is a steady-state thermal analysis of a circuit board.
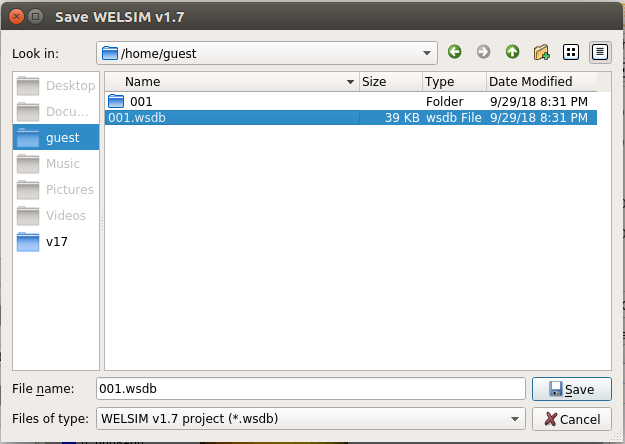
After the analysis is complete, the user can also save the project file on the remote server, as shown in the picture below:
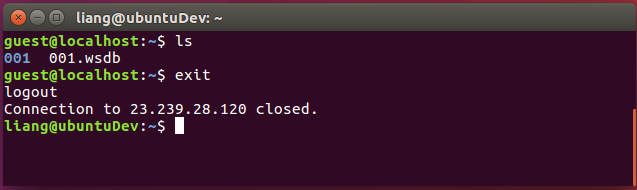
On the remote terminal window, view the saved project files.

When the remote job is done. You can type “exit” to end the remote connection. The terminal window will go back to the local machine.
Note that because the data stream of the running graphical software is relatively large, the speed may be affected by the network speed. Running the graphical application on the LAN will be faster.